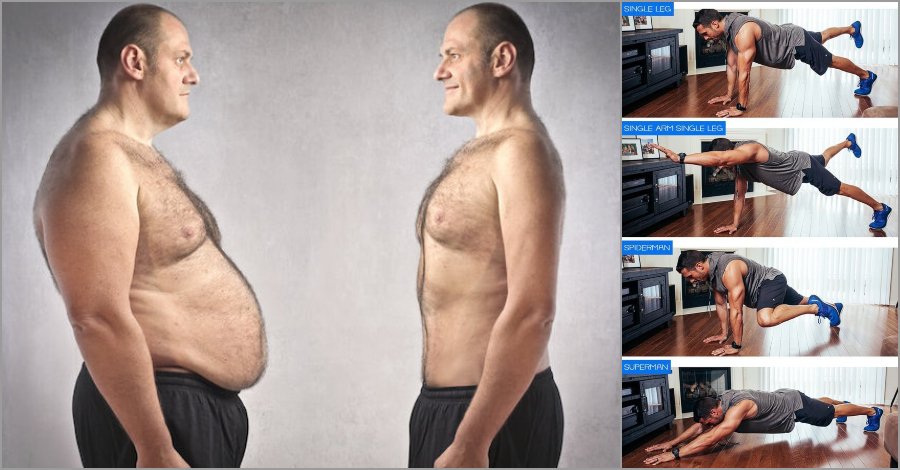
It is important to maintain strength in all ab muscles to help maintain your posture. Keeping strong abdominal muscles can also help reduce back pain, this takes pressure from your back muscles and puts them onto the core.
Abdominal muscles are a great benefit to the majority of the bodies overall mechanism. They allow movement, provide stability, support and balance. Strong abs can prevent back pain and other muscular problems. This is due to the core being central of the body and taking a good amount of pressure similar to the back muscles.
Abdominal Fats Explained:
Subcutaneous fat is the outer fat you can pinch, it is located between your skin and muscles. This fat is not dangerous it is just not pleasant for physical looks. Subcutaneous fat releases hormones into the blood at a slow rate and much slower concentration, this then releases a chemical called adiponectin.
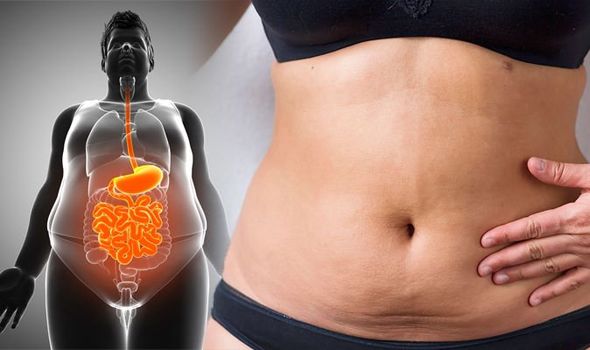
Adiponectin is a protein hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and also fatty acid oxidation, commonly known as the fat burning process. If you have small fat cells then they will stay small with this process. If you have larger cells, you would need to regulate your caloric intake and activities to help produce and speed up adiponictin.
Visceral fat is known as deep fat, this is stored underneath the subcutaneous fat. It is surrounding and wrapping itself around major organs. This fat can be dangerous as the fat cells can change the way your body operates. Eating too many calories has a major impact on creating this fat.
Will Ab Exercises Burn Belly Fat?
Targeted ab exercises are not very effective alone. Adding a combination of aerobic exercises, resistance training and a healthy diet (which includes plenty of protein and portion control) will help reduce belly fat.
While muscles grow and strengthen, studies show they won’t help you get rid of belly fat. This needs a combination of diet and exercise. One reason why targeted fat loss does not work is because muscle cells cannot use the fat contained in fat cells directly. Fat mass needs to be broken down with a clean diet.

Fat can come from anywhere in the body:
- Sit-ups and crunches seem like a good idea to target the abdominal area but it isn’t particularly effective for burning calories.
- Regular whole-body exercises will speed up your metabolism and burn calories and fat.
- Aerobic exercise and other cardio exercises may also be effective at targeting visceral belly fat.
- Moderate or high-intensity exercise can reduce belly fat mass.
- Low-intensity aerobic exercise or strength training is more beneficial towards the end as this will start to sculpt muscle and definition.
- You need to exercise often if you want to achieve significant results.
- Try moderate-intensity cardio for 30 minutes for five days a week.
- Try high-intensity cardio for 20 minutes for three days a week.
The muscle changes that take place in response to exercise also promote fat loss. Therefore the more muscle mass you build, the more fat you will burn and with a great diet your results will be achievable.
Will changing my diet help?
Good nutrition is essential if you want to lose body fat. Reduce your intake of processed foods. These are commonly packed with sugar and high-fructose corn syrup. Eating too much sugar can cause weight gain and increase your risk of metabolic diseases.

Focus on consuming higher amounts of protein, high-protein diets lead to a major reduction in hunger and will give feelings of fullness that may translate to a lower calorie intake. This is due to replacing the hunger hormone and boosting satiety hormones. A protein intake of around 25–30% of your daily calories may increase your metabolism by up to 100 calories per day.
Increasing your fibre intake is another good strategy for weight loss. Vegetables high in soluble fibre have been shown to help with weight loss. They contribute the increased feelings of fullness and decrease calorie intake over time.
Portion control is effective, when you consume whole foods, more fibre, protein and control your portions, you are more likely to cut back on calories. Achieving a long-term calorie deficit is beneficial.